ASPE ISSUE BRIEF: MEDICARE BENEFICIARY USE OF TELEHEALTH VISITS: EARLY DATA FROM THE START OF THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC
This ASPE issue brief examines changes in Medicare fee-for-service primary care visits and use of telehealth at the start of the COVID-19 public health emergency (PHE). This brief seeks to address the issue of how and whether the Medicare telehealth flexibilities introduced to address the COVID-19 pandemic may have helped maintain access to primary health care during the PHE. Data reflects visits up to early June in 2020.
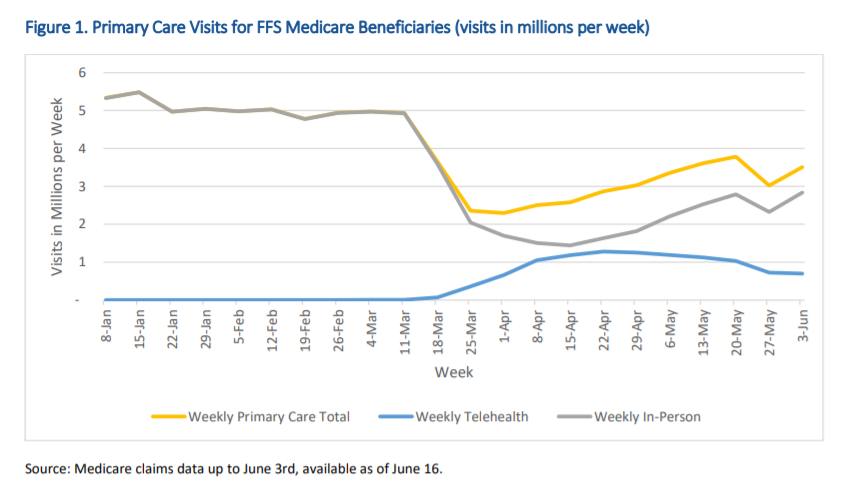
The analysis found Medicare primary care visits dropped precipitously from mid-March at the start of the pandemic, at the same telehealth visits increased for primary care. Nearly half of Medicare primary care visits were provided via telehealth in April, compared with less than one percent before the PHE in February. However telehealth use was lower in rural areas.
The report concludes there is evidence that Medicare’s new telehealth flexibilities played a critical role in helping to maintain access to primary health care services – when many beneficiaries and providers were concerned with transmission of COVID-19. Future research could examine whether these flexibilities were effective and if telehealth may have improved access to care and health outcomes among underserved beneficiaries.
 Loading...
Loading...